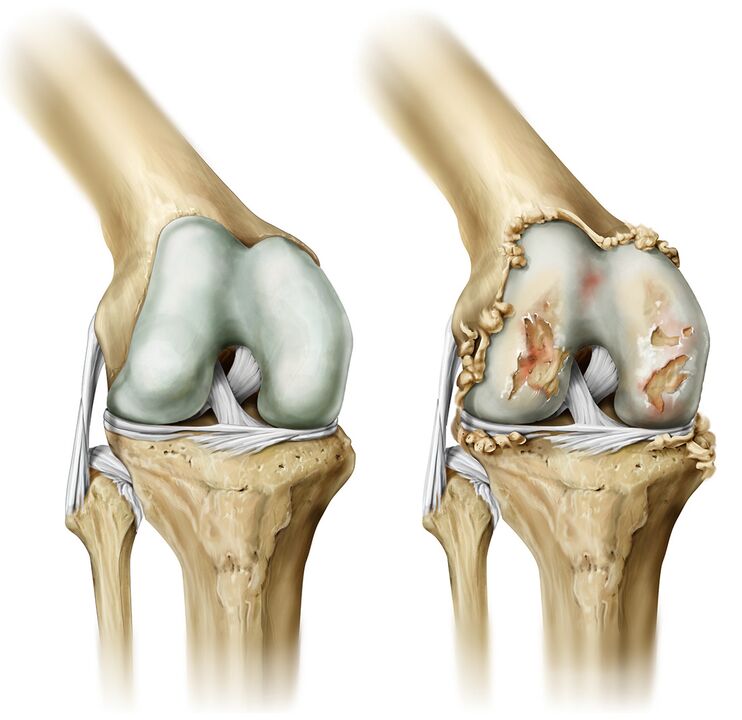
Arthrosis of the joints is a chronic disease characterized by the development of degenerative changes in the articular cartilage, as a result of which the bone tissue deforms. The joints of the big toes, hips and knees are the most affected.
disease symptoms
Causes of disease
The main reason for the development of arthrosis is the growth of the cartilage layer between the joint and the bone. The contributing factors are:
- Intense physical activity;
- Joint microtrauma;
- frequent fractures
- Wear tight shoes or high heels
- Congenital predisposition.
Diagnosis
The main method for diagnosing arthrosis is a carefully collected patient history (professional history).
Diagnosis is made based on patient examination and additional studies, including joint X-rays, arthroscopy, ultrasound, MRI, and CT scan.
complications
In the absence of timely medical care, arthrosis progresses and threatens with complications such as:
- Inflammation of tissues around the joint;
- Restricted mobility of affected joints;
- Degenerative changes in the hip joint;
- Changing the shape of the joints.
disease treatment
Treatment is prescribed to the patient depending on the degree of joint damage. Arthrosis therapy begins with pain relief.
In addition to analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to the patient. In addition to drug treatment, the patient takes a course of physiotherapy.
Massaging the affected limbs after the acute form of the inflammatory process has disappeared can reduce pain, normalize joint mobility, and relieve muscle spasm.
Physical therapy exercises are prescribed to relieve stiffness in the muscles, warm them up, and strengthen the patient's general condition. Exercise helps maintain correct posture and an even gait.
Treatment with a sanatorium is indicated in the period of stable remission. Mud baths, applications and other procedures help restore joint motor function and relieve pain.
If conservative methods of treatment do not bring the expected effect, the patient is prescribed surgical replacement of the joint. Stent grafts are made of a material that is not rejected by the human body. They allow you to fully restore the physiological functions of the affected joint.
Unique treatments: radiofrequency ablation and disruption of method integrity, disrupting the integrity of the nerve that causes pain.
Group of risk
The risk group includes people:
- Overweight;
- Varicose veins;
- Athletes;
- Pianists;
- Programmers.
Prophylaxis
The prevention of arthrosis is as follows:
- Good nutrition;
- Prevention of injuries and fractures;
- Limit the load on joints with hereditary predisposition;
- Body weight control;
- Wear shoes that fit.
diet and lifestyle
With a hereditary predisposition to the development of arthrosis, as well as during an exacerbation of the disease, it is necessary to adjust the diet. It is recommended to include in the diet sea fish (sardines, salmon, tuna), fresh vegetables and fruits, cereals. Limit baked goods, fatty meats, chocolate and alcohol.
It is recommended to spend more time outdoors and not expose your joints to increased physical activity.



































